Difference between revisions of "Coefficients/Potentiometers"
From TheAnalogThing
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
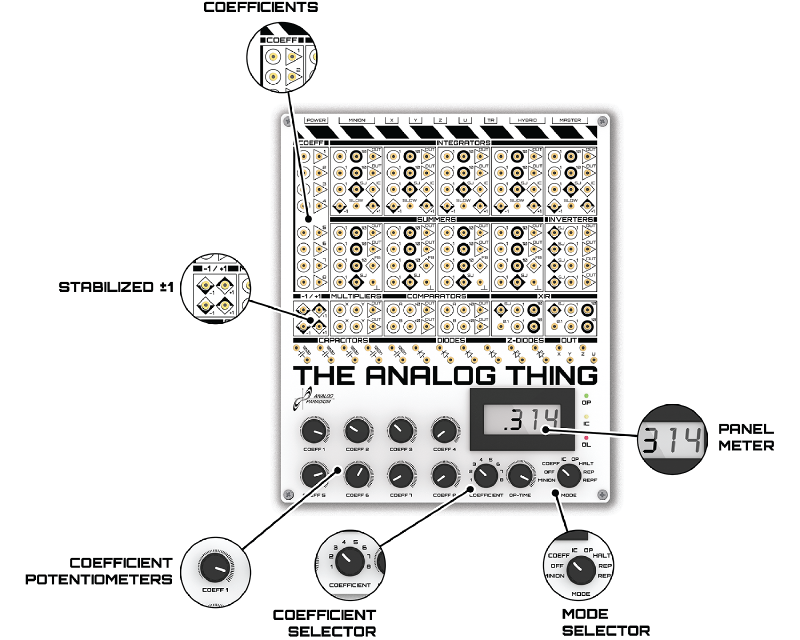
| − | '''Coefficients''' are quantitative parameters that enter analog computations | + | '''Coefficients''' are quantitative parameters that enter analog computations. [[The Analog Thing]] features eight coefficient potentiometers, allowing the use of up to eight coefficients in an analog program on a single THAT. Using the potentiometers, each coefficient can be set to any value between <code>0</code> and <code>+1</code>. An input to a coefficient potentiometer is multiplied by the value the coefficient potentiometer is set to such that their output is given by <code>output = coefficient * input</code>. |
Several sections of the THAT user interface relate to the use of coefficient potentiometers, as shown in Figure 1: | Several sections of the THAT user interface relate to the use of coefficient potentiometers, as shown in Figure 1: | ||
Revision as of 05:20, 30 August 2021
Coefficients are quantitative parameters that enter analog computations. The Analog Thing features eight coefficient potentiometers, allowing the use of up to eight coefficients in an analog program on a single THAT. Using the potentiometers, each coefficient can be set to any value between 0 and +1. An input to a coefficient potentiometer is multiplied by the value the coefficient potentiometer is set to such that their output is given by output = coefficient * input.
Several sections of the THAT user interface relate to the use of coefficient potentiometers, as shown in Figure 1:
- The
COEFFICIENTSsection. This is the area labelledCOEFFon your THAT. It contains the input and output sockets for the coefficient potentiometers. - The
COEFFICIENT POTENTIOMETERSsection. It contains the eight rotary knobs by which coefficients can be set. - The
MODE SELECTOR. - The
COEFFICIENT SELECTOR. It is used to select the coefficient value to display on thePANEL METERwhen theMODE SELECTORis in theCOEFFposition. - The
PANEL METER.
To familiarize yourself with the use of coefficient potentiometers, follow these steps:
- Set the
MODE SELECTORto positionCOEFFand set theCOEFFICIENT SELECTORto position1. This connects the output of potentiometerCOEFF 1to thePANEL METER. - Use a patch cable to connect one of the
+1sockets in theSTABILIZED ±1section to the input (circle) associated with potentiometerCOEFF 1in theCOEFFICIENTSsection (i.e., the uppermost circled socket in the section labelledCOEFFon your THAT). - Change the position of the
COEFF 1knob in theCOEFFICIENT POTENTIOMETERSsection and observe the value displayed on thePANEL METER. The displayed value is available at the output (triangle) associated with potentiometerCOEFF 1in theCOEFFICIENTsection. - Remove the patch cable plug from the
+1socket in theSTABILIZED ±1section and plug it into one of the-1sockets in in theSTABILIZED ±1. - Again, change the position of the
COEFF 1knob in the potentiometer section and observe the value displayed on thePANEL METER. - Set the
COEFFICIENT SELECTORto any one of the other potentiometers (say, 4). - Use a patch cable to connect either of the
-1sockets in theSTABILIZED ±1with the input (circle) associated with the with the coefficient potentiometer you have chosen using theCOEFFICIENT SELECTOR(say, 4). - Change the position of the coefficient potentiometer knob associated with the coefficient you have chosen using the
COEFFICIENT SELECTOR(say, 4) and again observe the value displayed on thePANEL METER.