Difference between revisions of "Oscilloscope"
(+3 links from Dirk) |
(Moving text from Software Oscilloscopes) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | An '''Oscilloscope''' is an essential measurement device when doing analog computing. Nevertheless, even cheap entry level devices cost more then 200 EUR. This page shall document | + | An '''Oscilloscope''' is an essential measurement device when doing analog computing. Nevertheless, even cheap entry level devices cost more then 200 EUR. This page shall document how to use oscilloscopes with [[THAT]] and gives recommendations about devices are suitable for working with [[The Analog Thing]]. If you don't want to spend money on an oscilloscope, a [[Software Oscilloscope]] maybe an alternative. |
| − | == | + | == Using Oscilloscopes == |
| + | To watch and measure the values and curves produced during an analog computation or simulation you need additional instruments. The Analog Thing contains a [[voltmeter]] as instrument to setup the coordinates or OP_TIME values. Depending on the [[modes|mode of operation]] in '''REP''' with predefined operation time or '''OP''' with infinite operation this display may be useful for static or slow moving values only. | ||
| + | |||
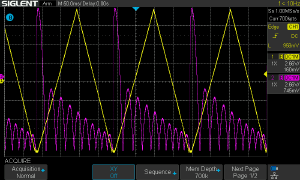
| + | [[Image:DSO_Yt_display.png|thumb|typical Yt display of signals on a DSO]] | ||
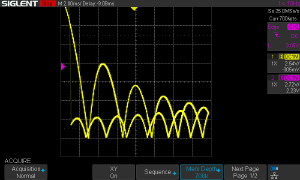
| + | To measure faster events or display signal curves the best tool is an '''oscilloscope'''. For longer operation times (REP, 0.1-10s) a digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) is preferred rather than an analog oscilloscope with a cathode ray tube (CRT). These DSO did get cheaper in the last years but useful DSO's with minimum 2 channels and XY mode are in the price range of about 150-300 € up. XY mode is useful for many applications and allow a better view of complex signals than displaying them just over the time in Yt mode. The typical Lissajous figures for example require the XY mode. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:DSO_XY_display.png|thumb|typical XY display of the same signals above]] | ||
| + | There are low cost oscilloscope on the market as well in the range of 40-100 € but these come with missing features and have mostly only one channel to display like DSO 138 or missing XY mode like DS 212/213. This is only partly useful with analog computations or simulations and all theses cheap handhelds have only a very small display. Some low cost oscilloscopes come without a display and are connected to a computer as display by software. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Requirements for Oscilloscopes with The Analog Thing == | ||
| + | === Minimum requirements (cheap devices) === | ||
| + | * analog oscilloscope with CRT display or software display while connected to computer | ||
| + | * 1 or 2 channels | ||
| + | * XY display mode | ||
| + | * 100 kHz bandwith | ||
| + | |||
| + | Recommendations: | ||
| + | * [https://www.meilhaus.de/picoscope-2000.htm Picoscope] (125€ entry prize) | ||
| + | * [https://store.digilentinc.com/analog-discovery-2-100msps-usb-oscilloscope-logic-analyzer-and-variable-power-supply/ Analog Discovery 2] (280€ for academic) | ||
| + | * [https://www.analog.com/en/design-center/evaluation-hardware-and-software/evaluation-boards-kits/adalm2000.html#eb-overview ADMAL2000] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Further cheap alternatives: | ||
* HS101 http://hscope.martinloren.com/HS101-oscilloscope.html | * HS101 http://hscope.martinloren.com/HS101-oscilloscope.html | ||
* DroidOscillo https://hackaday.io/project/26360-android-oscilloscope-droidoscillo | * DroidOscillo https://hackaday.io/project/26360-android-oscilloscope-droidoscillo | ||
| Line 7: | Line 28: | ||
* SmartScope https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/751733865/smartscope-reinventing-the-oscilloscope | * SmartScope https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/751733865/smartscope-reinventing-the-oscilloscope | ||
| − | == | + | === Medium requirements === |
| − | * | + | * 4 channels or separate trigger input |
| − | + | * DSO type (digital storage) | |
| − | + | ||
| + | == Alternatives == | ||
| + | There is a cheaper alternative for beginners with low budget while using a [[Soundcard Oscilloscope]] software. These solutions are based on using a sound input of the computer and a software to display the signal while reading digitized data of AD converters on the soundcard. If your computer contains a sound input you are lucky as you can get the software for free. Unfortunately many newer computers no more have classical sound input in stereo (so called 'line-in') and if so it is mostly only a microphone input as mono (1 channel instead of 2). This is the same lack as an oscilloscope with only 1 input channel. | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Hardware]] | [[Category:Hardware]] | ||
Revision as of 09:06, 6 August 2021
An Oscilloscope is an essential measurement device when doing analog computing. Nevertheless, even cheap entry level devices cost more then 200 EUR. This page shall document how to use oscilloscopes with THAT and gives recommendations about devices are suitable for working with The Analog Thing. If you don't want to spend money on an oscilloscope, a Software Oscilloscope maybe an alternative.
Using Oscilloscopes
To watch and measure the values and curves produced during an analog computation or simulation you need additional instruments. The Analog Thing contains a voltmeter as instrument to setup the coordinates or OP_TIME values. Depending on the mode of operation in REP with predefined operation time or OP with infinite operation this display may be useful for static or slow moving values only.
To measure faster events or display signal curves the best tool is an oscilloscope. For longer operation times (REP, 0.1-10s) a digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) is preferred rather than an analog oscilloscope with a cathode ray tube (CRT). These DSO did get cheaper in the last years but useful DSO's with minimum 2 channels and XY mode are in the price range of about 150-300 € up. XY mode is useful for many applications and allow a better view of complex signals than displaying them just over the time in Yt mode. The typical Lissajous figures for example require the XY mode.
There are low cost oscilloscope on the market as well in the range of 40-100 € but these come with missing features and have mostly only one channel to display like DSO 138 or missing XY mode like DS 212/213. This is only partly useful with analog computations or simulations and all theses cheap handhelds have only a very small display. Some low cost oscilloscopes come without a display and are connected to a computer as display by software.
Requirements for Oscilloscopes with The Analog Thing
Minimum requirements (cheap devices)
- analog oscilloscope with CRT display or software display while connected to computer
- 1 or 2 channels
- XY display mode
- 100 kHz bandwith
Recommendations:
- Picoscope (125€ entry prize)
- Analog Discovery 2 (280€ for academic)
- ADMAL2000
Further cheap alternatives:
- HS101 http://hscope.martinloren.com/HS101-oscilloscope.html
- DroidOscillo https://hackaday.io/project/26360-android-oscilloscope-droidoscillo
- DSO-138 https://www.reichelt.de/dso-138-oszilloskop-1-kanal-200-khz-12-bit-joy-it-dso-138-p209775.html?&trstct=pol_0&nbc=1
- SmartScope https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/751733865/smartscope-reinventing-the-oscilloscope
Medium requirements
- 4 channels or separate trigger input
- DSO type (digital storage)
Alternatives
There is a cheaper alternative for beginners with low budget while using a Soundcard Oscilloscope software. These solutions are based on using a sound input of the computer and a software to display the signal while reading digitized data of AD converters on the soundcard. If your computer contains a sound input you are lucky as you can get the software for free. Unfortunately many newer computers no more have classical sound input in stereo (so called 'line-in') and if so it is mostly only a microphone input as mono (1 channel instead of 2). This is the same lack as an oscilloscope with only 1 input channel.